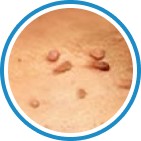
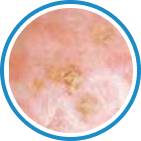
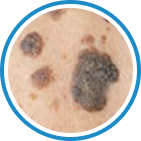
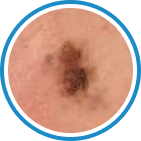
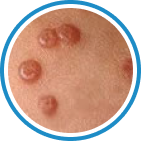
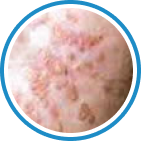
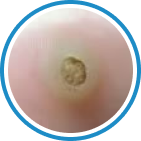
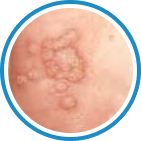
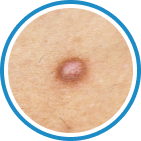
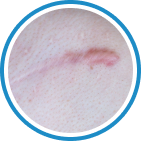
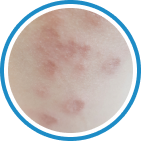
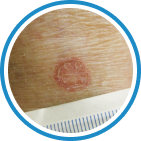
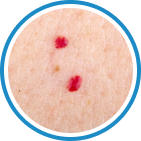
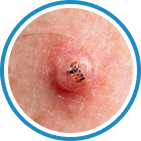
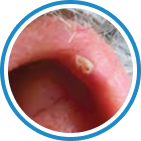
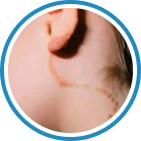
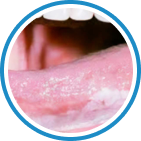
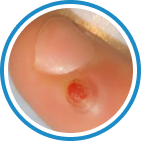
Indications
Hydrozid® is the right combination of traditional Cryotherapy and Cryosurgery with modern aerosol technology. It provides low risk, rapid and effective Cryosurgical treatment for a wide range of warts, common skin lesions and some mucosal lesions.